React LifeCycle
0. 그 전에…
- 라이프사이클은 stateful 컴포넌트에만 적용이 가능하다.
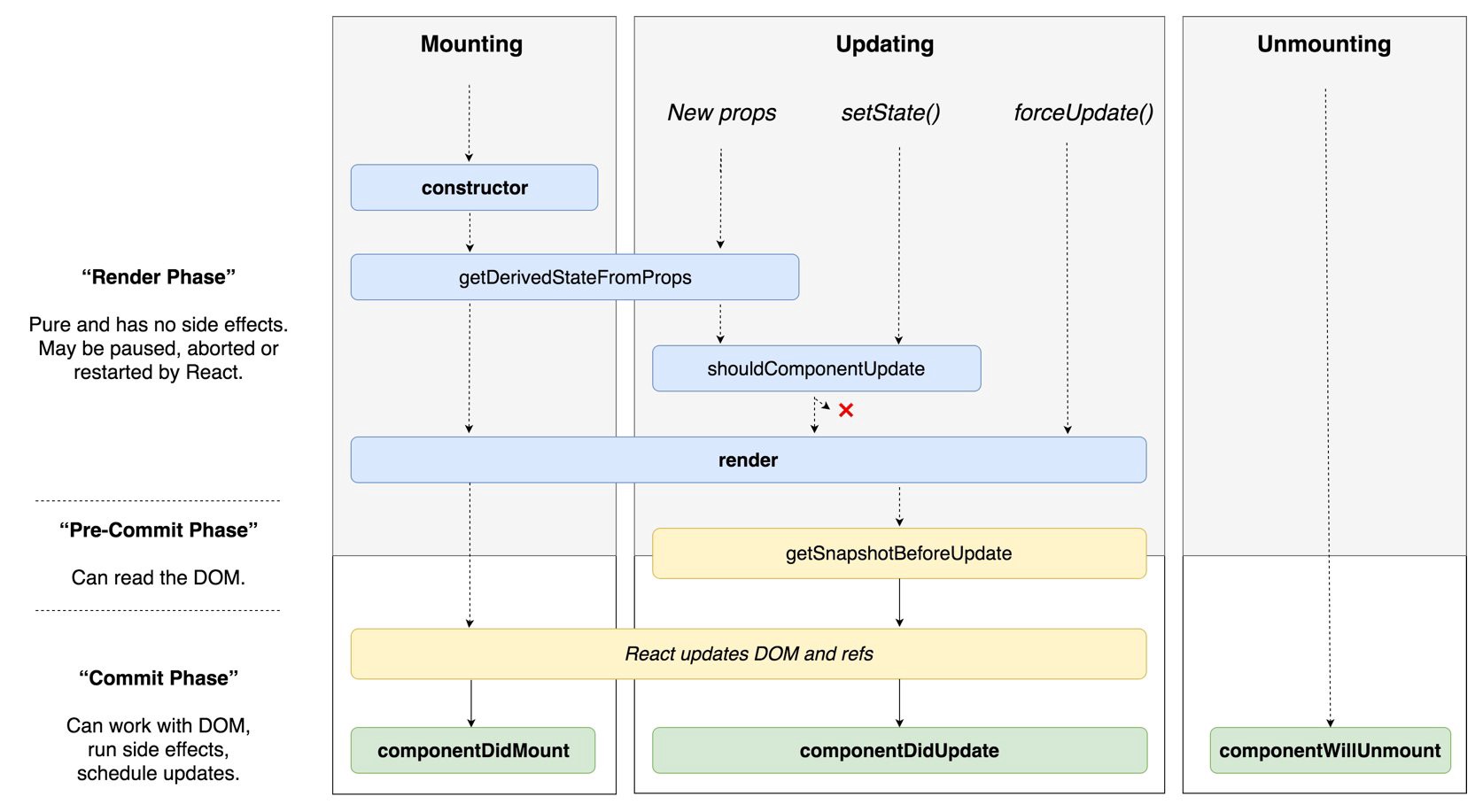
1. 컴포넌트 첫 생성(Mount)
컴포넌트가 처음 생성될 때 시작된다.
-
constructor : 컴포넌트 생성자 함수. 컴포넌트가 처음 생성될 때 호출된다. 주로 하는 일은 state 초기 설정.
-
render : Virtual Dom 에 생성된 컴포넌트를 렌더링한다.
-
해당 컴포넌트를 렌더링하는 과정에서 자식 컴포넌트가 있으면 자식 컴포넌트의 lifecycle 을 실행한다.
-
자식 컴포넌트가 생성이 끝나면 componentDidMount 메소드를 실행한다. 이 메소드에서 side effect(axios 등)을 실행할 수 있다.(하지만 setState 는 쓰지 말 것! <= https://www.udemy.com/react-the-complete-guide-incl-redux/learn/v4/questions/4022072)
class MyComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props); // Component클래스의 생성자를 override했기 때문에 super(props)로 기본 설정을 해주어야 한다.
this.state = {
fruits: ['apple', 'banana']
};
}
getDerivedStateFromProps() {}
componentDidMount() {
/*
this.setState({
fruits: [...this.state.fruits, "mango"]
})
이런식으로 instant하게 사용하지 말라는 뜻 => 즉각적인 re-render 때문에 성능 이슈가 생긴다고 하네요.
*/
axios.get(url).then(response => {
this.setState({
fruits: [...this.state.fruits, response.data]
});
});
// 이렇게 async 안에서 사용하는 것은 괜찮습니다.
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>My Component</h1>
<ChildComponent />
</div>
);
}
}
2. 컴포넌트 수정(Update)
컴포넌트가 받는 props 가 바뀌거나 state 가 수정될 경우 시작된다.
-
getDerivedStateFromProps: props 값을 state 로 동기화 시켜줘야 할 때 사용한다. props 값이 업데이트되었을 경우에만 호출된다.
-
shouldComponentUpdate: 부모 컴포넌트가 업데이트로 re-render 될 경우 포함된 모든 자식 컴포넌트도 re-render 된다. 물론 변화가 없으면 real DOM 까지 영향을 미치지는 않고 Virtual DOM 만 re-render 하는 선에서 끝나지만, 어쨌거나 필요없는 행동을 한 것이다. 이 메소드는 기본적으로 true 를 return 하는데, 경우에 따라 false 를 리턴하게 짜 주면 굳이 필요하지않는 re-render 를 막을 수 있다.
-
render: 생성때와 같은 render 메소드. 다만 업데이트는 새 virtual Dom 과 기존 DOM 을 비교해 다른 부분만을 렌더링해준다.
-
componentDidUpdate: 실제 업데이트가 끝나고 난 뒤 실행되는 메소드. 이 메소드 전 까지는 this.state 와 this.props 가 업데이트 전의 상태이다가 여기서부터 업데이트 된 상태로 바뀐다.
class MyComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props); // Component클래스의 생성자를 override했기 때문에 super(props)로 기본 설정을 해주어야 한다.
this.state = {
fruits: ['apple', 'banana']
};
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState) {
//인스턴스 메소드가아닌 클래스 메소드이므로 this사용 불가
// 따라서 state를 바꾸려면 this.setState가 아닌 값을 리턴해주면 됨
if (nextProps.fruits[-1] !== prevState.fruits[-1]) {
return { fruits: [...nextProps.fruits] };
}
return null; //바꿀것이 없으면 null리턴.
}
componentDidMount() {
/*
this.setState({
fruits: [...this.state.fruits, "mango"]
})
이런식으로 instant하게 사용하지 말라는 뜻 => 즉각적인 re-render 때문에 성능 이슈가 생긴다고 하네요.
*/
axios.get(url).then(response => {
this.setState({
fruits: [...this.state.fruits, response.data]
});
});
// 이렇게 async 안에서 사용하는 것은 괜찮습니다.
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
// componentDidUpdate 메소드 전 까지는 this.state, this.props를 하면 업데이트 되지않은 상태이므로 매개변수로 받은 nextProps, nextState를 이용해서 새 값에 접근할 수 있다.
if (this.state.fruits.length === nextState.fruits.length) {
return false; // fruits배열 개수가 같으면 update중지.
}
return true;
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
//여기서부턴 this.state, this.props는 업데이트가 된 상태. 이전의 값에는 매개변수로 접근할 수 았다.
//또한 side effect도 이곳에서 실행할 수 있다.
}
render() {
const fruits = this.state.fruits.map((fruit, index) => (
<li key={index}>{fruit}</li>
));
return (
<div>
<h1>My Component</h1>
<ul>{fruits}</ul>
<ChildComponent />
</div>
);
}
}
3. 컴포넌트 제거(Unmount)
- componentWillUnmount: 주로 등록했었던 이벤트를 제거하고, 만약에 setTimeout 을 걸은것이 있다면 clearTimeout 을 통하여 제거를 합니다. 추가적으로, 외부 라이브러리를 사용한게 있고 해당 라이브러리에 dispose 기능이 있다면 여기서 호출해주시면 됩니다. side effect 도 여기서 사용가능합니다.

